Unlock the secrets of vCenter Server resilience with VCHA! Ever wondered how VCHA works its magic in safeguarding your server against failures? From unraveling its architecture to exploring the benefits of deployment, this blog post will take you on an insightful journey through the workings of VCHA. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of vCenter High Availability!
Key Takeaways
- VCHA is based on a multi-nodes architecture with an active-passive configuration plus a Witness node, designed to reduce downtime when vCSA fails.
- VCHA requires vCenter server 6.5 or later, deployment size small or bigger, and a network latency of less than 10ms.
- VMware HA continuously monitors all ESX Server hosts in a cluster and detects failures, initiating the process of restarting affected virtual machines on other hosts.
- The difference between VCHA basic and advanced lies in the configuration process, with basic automatically creating and configuring clones, while advanced requires user intervention.
- VCenter High Availability (VCHA) protects vCenter Server Appliance against host and hardware failures, reducing downtime significantly during patching.
- When configuring VCHA, the wizard creates a three-node cluster containing Active, passive, and Witness nodes.
VCHA: Enhancing vCenter Server Resilience against Failures
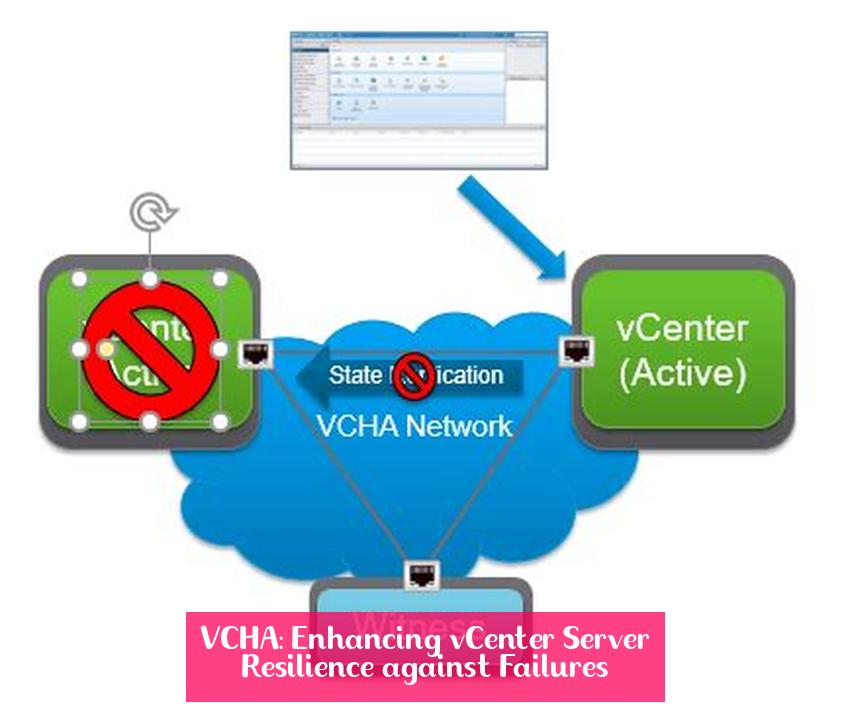
VCHA stands for vCenter High Availability, a robust solution designed to safeguard vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) against host and hardware failures. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of VCHA, exploring its inner workings, requirements, and benefits. Learn how VCHA ensures continuous availability of vCenter Server, minimizing downtime and maximizing uptime for your virtualized environment.
More updates: Are Stray Cats Homeless? Understanding Their Plight and How to Help
Unveiling the Architecture of VCHA
VCHA’s architecture centers around a multi-node setup, featuring an active node, a passive node, and a witness node. The active node assumes the primary role of running vCenter Server, while the passive node stands ready as a backup, prepared to assume the active role in the event of a failure. The witness node plays a crucial role in maintaining data integrity and facilitating seamless failover between the active and passive nodes.
Prerequisites for Implementing VCHA
To harness the power of VCHA, certain requirements must be met:
Discover: VCHA’s Debut: A New Era in Global Pop Music
- vCenter Server 6.5 or later: VCHA demands a robust foundation, and vCenter Server 6.5 or subsequent versions provide the necessary stability and functionality.
- Deployment Size: VCHA requires a deployment size of small or larger. Tiny deployments, often utilized for testing purposes, are not recommended for production environments due to their limited resources.
- Network Latency: The network latency between VCHA nodes should ideally be less than 10 milliseconds. This ensures rapid communication and minimizes the impact of network delays on failover processes.
- Dedicated Network: VCHA requires a dedicated network separate from the management network. This segregation enhances security and optimizes performance by preventing network congestion and conflicts.
Delving into the Workings of VM HA
VMware HA (High Availability) plays a pivotal role within VCHA, continuously monitoring all ESX Server hosts within a cluster. It acts as a vigilant sentinel, detecting failures promptly. Upon detecting a failure, VM HA triggers the process of restarting affected virtual machines on other healthy hosts, ensuring service continuity and minimizing downtime.
Distinguishing between Basic and Advanced VCHA Configurations
VCHA offers two configuration options: Basic and Advanced. The primary distinction lies in the cloning process:
Kpop Trends — Unlocking the Posse Scholarship: What GPA Do You Need and How to Improve It
- Basic Configuration: In a basic VCHA setup, the configuration process automates the creation and configuration of passive and witness nodes, simplifying the deployment process.
- Advanced Configuration: The advanced VCHA configuration requires manual intervention. The user assumes responsibility for creating and configuring the passive and witness nodes, providing greater flexibility and control over the deployment process.
Benefits of Deploying VCHA
VCHA offers a plethora of advantages that enhance the reliability and availability of vCenter Server:
- Minimized Downtime: VCHA significantly reduces downtime during patching or maintenance activities. By seamlessly transitioning to a backup node, VCHA ensures continuous availability of vCenter Server, preventing service disruptions.
- Enhanced Fault Tolerance: VCHA’s multi-node architecture provides resilience against hardware failures and host outages. If the active node encounters an issue, the passive node swiftly takes over, maintaining uninterrupted vCenter Server operations.
- Simplified Management: VCHA simplifies the management of vCenter Server by providing a centralized platform for monitoring and managing the entire VCHA cluster. This streamlined approach reduces administrative overhead and enhances operational efficiency.
Also read Anton Du Beke’s Hair Transplant Journey: A Detailed Account of His Transformation
Conclusion
VCHA, a cornerstone of vSphere’s high availability strategy, safeguards vCenter Server against hardware and host failures, minimizing downtime and ensuring service continuity. By leveraging VCHA’s multi-node architecture and advanced capabilities, organizations can achieve superior resilience and availability for their virtualized environments, maximizing uptime and optimizing performance.
What are the requirements for VCHA?
VCHA requires vCenter server 6.5 or later, deployment size small or bigger, and a network latency of less than 10ms. The network for VCHA must be different from the management network.
How does VM HA work?
VMware HA continuously monitors all ESX Server hosts in a cluster and detects failures. When a failure is detected, the process of restarting affected virtual machines on other hosts is initiated.
What is the difference between VCHA basic and advanced?
In a Basic configuration, VCHA automatically creates and configures the clones. In an Advanced configuration, the user is responsible for creating and configuring the clones.
What is VCHA VMware?
VCenter High Availability (VCHA) is designed to protect vCenter Server Appliance against host and hardware failures, reducing downtime significantly during patching. It is based on a multi-nodes architecture with an active-passive configuration plus a Witness node.







