Unlocking the potential of vCenter High Availability (VCHA) can seem like a daunting task, but fear not! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of enabling VCHA, from understanding its benefits to troubleshooting common issues. So, grab a cup of coffee and get ready to dive into the world of VCHA configuration – it’s easier than you think!
Key Takeaways
- To enable vCenter High Availability (VCHA), log in to the Active node using the vSphere Web Client, right-click the vCenter Server object, select vCenter HA Settings, and click Configure.
- When putting VCHA in maintenance mode, log in to vSphere Web Client, select vCenter Server, go to vCenter HA Configuration, click Edit to modify the settings, and choose Maintenance Mode.
- To check if vCenter HA is enabled, open the vSphere Web Client, select Configure, then vCenter HA, and click vCenter HA Monitoring to access the monitoring window displaying the current status of the nodes.
- To enable DRS and HA, browse to the cluster in the vSphere Client, click Configure, select vSphere DRS under Services, click Edit, and then turn on vSphere DRS and vSphere HA.
Understanding vCenter High Availability (VCHA)
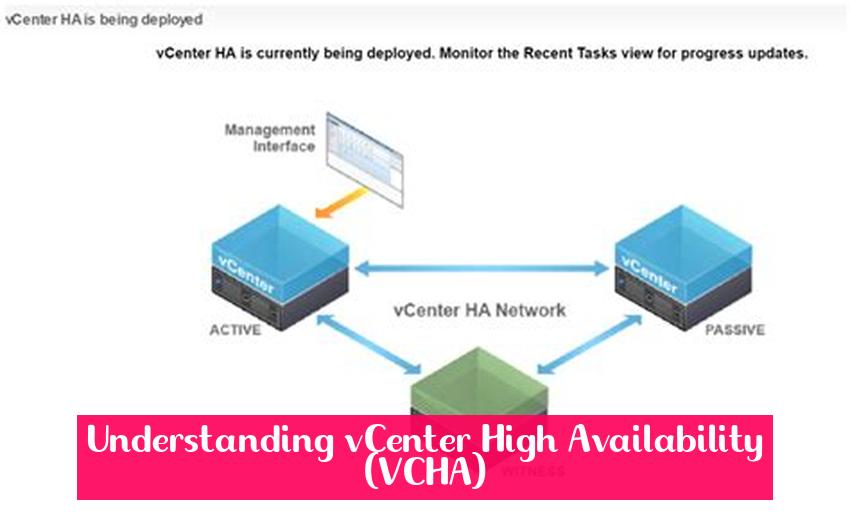
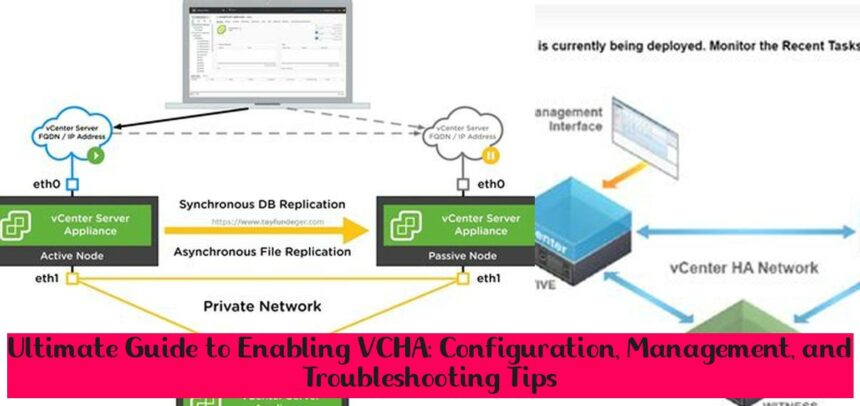
vCenter High Availability (VCHA) is a crucial feature in VMware’s virtualization platform that ensures continuous availability of the vCenter Server, the central management component for virtualized environments. By deploying VCHA, organizations can safeguard their virtual infrastructure against hardware failures, network disruptions, or planned maintenance activities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key aspects of VCHA, including its benefits, configuration steps, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting techniques.
More related > VCHA’s Debut: A New Era in Global Pop Music
Benefits of Deploying VCHA
Implementing VCHA offers several advantages that enhance the resilience and reliability of virtualized environments:
- High Availability: VCHA eliminates single points of failure by deploying two vCenter Server instances, known as the Active and Passive nodes. If the Active node encounters an issue, the Passive node seamlessly takes over, ensuring uninterrupted management of virtual machines and infrastructure components.
- Load Balancing: VCHA enables load balancing of management tasks between the Active and Passive nodes. This distribution improves performance and scalability, especially in large and complex virtual environments with numerous virtual machines and hosts.
- Simplified Management: VCHA provides a centralized management interface for both the Active and Passive nodes, allowing administrators to manage the entire virtual infrastructure from a single console. This simplifies administrative tasks and streamlines troubleshooting processes.
- Planned Maintenance: With VCHA in place, administrators can perform planned maintenance activities, such as patching or upgrading the vCenter Server software, without disrupting the availability of virtual machines or services. This flexibility enhances operational efficiency and minimizes downtime.
Configuring VCHA: A Step-by-Step Guide
Deploying VCHA involves a series of configuration steps to ensure proper functionality and high availability. Follow these steps to set up VCHA in your virtual environment:
Now Trending — Unlocking the Posse Scholarship: What GPA Do You Need and How to Improve It
1. Prerequisites:
- Two Physical Servers: You will need two physical servers or virtual machines to host the Active and Passive vCenter Server nodes.
- Shared Storage: A shared storage solution, such as a SAN or NAS, is required to store the vCenter Server data, including virtual machine configurations and logs.
- Dedicated Network: A dedicated network is recommended for VCHA traffic to ensure reliable communication between the Active and Passive nodes.
2. Deploying the Active and Passive Nodes:
- Install vCenter Server: Install vCenter Server on both the Active and Passive nodes. Ensure that both nodes have the same version and build of vCenter Server.
- Configure Networking: Assign IP addresses from the dedicated network to the VCHA management interfaces on both nodes.
- Configure Shared Storage: Configure shared storage access for both nodes to ensure they can access the same data.
3. Configuring VCHA:
- Log in to the Active Node: Access the Active node using the vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client.
- Enable VCHA: Right-click the vCenter Server object, select “vCenter HA Settings,” and click “Configure.”
- Configure VCHA Network: Specify the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for the VCHA network.
- Configure Witness Node: Select a witness node, which can be a physical server or a virtual machine, to provide quorum in case of network partitions.
- Complete Configuration: Review the configuration summary and click “Finish” to enable VCHA.
Managing and Troubleshooting VCHA
Once VCHA is configured, it requires ongoing management and troubleshooting to ensure its continued availability and effectiveness. Here are some key considerations:
1. Monitoring VCHA Status:
- vCenter HA Monitoring Window: Access the vCenter HA Monitoring window to monitor the status of the Active, Passive, and Witness nodes, as well as the overall health of the VCHA cluster.
- Notifications: Configure alerts and notifications to be informed about VCHA events, such as node failures or network issues.
2. Maintenance and Updates:
- Maintenance Mode: To perform maintenance tasks on the Active node, such as patching or upgrading, place the node in maintenance mode. This temporarily transfers the active role to the Passive node.
- Updates: Apply software updates and patches to both the Active and Passive nodes to ensure they are running the latest and most secure versions of vCenter Server.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues:
- Node Communication Issues: Verify network connectivity between the Active and Passive nodes and the witness node. Ensure that firewalls are not blocking communication on the VCHA network.
- Witness Node Failure: If the witness node fails, the VCHA cluster may experience split-brain syndrome. Address witness node issues promptly to restore quorum and maintain VCHA functionality.
- Data Replication Issues: Monitor data replication between the Active and Passive nodes to ensure that data is synchronized. Address any replication issues to prevent data inconsistencies.
Conclusion
VMware vCenter High Availability (VCHA) plays a vital role in ensuring the continuous availability and resilience of virtualized environments. By deploying VCHA, organizations can safeguard their virtual infrastructure against hardware failures, network disruptions, and planned maintenance activities. With careful planning, configuration, and ongoing management, VCHA provides a reliable and scalable platform for managing virtualized workloads. By following the steps and considerations outlined in this guide, you can successfully implement and maintain VCHA in your virtual environment, ensuring high availability and minimizing downtime.
How do I deploy Vcha?
Answer: To deploy vCenter High Availability, log in to the Active node using the vSphere Web Client, right-click the vCenter Server object, select vCenter HA Settings, and click Configure. Then, select the Advanced configuration option and enter the HA Network IP and subnet mask for the Passive Node.
How do I put Vcha in maintenance mode?
Answer: To put VCHA in maintenance mode, log in to the vSphere Web Client, select vCenter Server, go to vCenter HA Configuration, click Edit to modify the settings, and choose Maintenance Mode. Click OK to save the changes.
How do I know if vCenter HA is enabled?
Answer: To check if vCenter HA is enabled, open the vSphere Web Client, select Configure, then vCenter HA, and click vCenter HA Monitoring to access the monitoring window displaying the current status of the Active, Passive, and Witness nodes.
How do I enable DRS and HA?
Answer: To enable DRS and HA, browse to the cluster in the vSphere Client, click Configure, select vSphere DRS under Services, click Edit, and then turn on vSphere DRS and vSphere HA. Click OK to save the changes.